差分进化算法的简单介绍,学习笔记,记录成长。
一. 算法简介
差分进化算法(Differential Evolution)是一种用于最佳化问题的后设启发式算法。本质上,它是一种基于实数编码的具有保优思想的贪婪算法
差分进化算法类似遗传算法,包含变异、交叉操作,淘汰机制,而差分进化算法与遗传算法不同之处,在于变异的部分是随机选取两个解成员变数的差异,经过伸缩后加入当前解成员的变数上,因此差分进化算法无须使用概率分布产生下一代解成员。1997年,Storn与Price在全域最佳化国际学术期刊(Journal of global optimization)发表了差分进化算法 –维基百科
差分演化算法是演化算法中的一种。演化算法是一种基于种群的启发式算法,其算法过程是模拟生物进化来进行设计的,下面是演化算法的基本结构,其中,t 表示演化代数,P(t) 表示第 t 代群体,每一个个体Xi ( i = 1,2,…,N) 代表一个解,每一个种群代表一组解。
begin
t = 0;
随机初始化种群P(t) = {X1, X2, ... , XN};
计算 P(t) 中所有个体的适应性;
while(不满足停止条件)
{
将各种遗传算法(如选择、交叉、变异等)作用于群体P(t),形成新的群体P(t+1);
计算群体P(t+1)中,所有个体的适应性;
t = t + 1;
}
输出结果;
end
总体上看,演化算法主要涉及7个部分的设计:个体的编码表示、初始化种群、适应值函数、遗传操作、选择策略、控制参数以及停止条件。
差分进化算法其整体框架与一般演化算法类似,采用实数编码方式,主要在变异和交叉的遗传操作上略有不同。其变异操作的主要思想是利用种群中其他个体的向量差对目标个体(Target Individual) 进行变异操作,得到变异后的个体–变异个体(Mutant Individual) ;对变异个体和目标个体进行类似一般演化算法的交叉操作,的阿斗一个新个体;通常使用锦标赛策略选择目标个体和新个体中优胜的个体,保留到下一代。
二. 算法详解
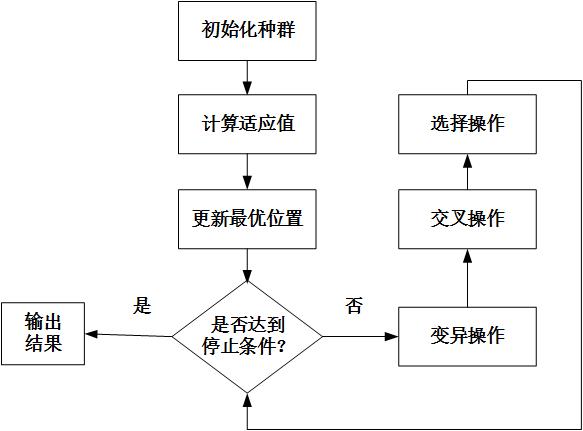
差分演化算法的主要操作步骤:
 <
<
设某优化问题的维度为D,种群规模为N,做一下规定:
第 t 代的第 i 个个体为:$X_i(t)$ ,它变异后的个体为:$H_i(t+1)$,然后二者杂交后的新个体为:$V_i(t+1)$,差分进化算法的基本变异操作可表示为: $$Hi(t+1)=X{p1}(t)+F(X{p2}(t)-X{p3}(t))$$
其中,$X{p1}(t),X{p2}(t)$和$X_{p3}(t)$是从种群中随机选择的三个互不相等,且均与$X_i(t)$不相等的个体。F为缩放因子,用于控制差异化向量对变异操作的影响,取值范围在[0,2]区间内。
差分进化算法的交叉操作主要分为”bin”型和”exp”型两类。“bin”型交叉操作类似于遗传算法中的均匀交叉,每一位都根据概率选择,其概率分布满足二项式,如下公式:
$$V{ij}(t+1)=\left{
\begin{array}{rcl}
H{ij}(t+1) & & { if(rand1{ij}\le CR) or(j==rand(i))}\
X{ij}(t) & & {otherwise}\
\end{array} \right.
$$
其中,CR为交叉概率,$rand1_{ij}$为0到1之间的随机数,rand(i)为1到D之间的随机整数。
而“exp”扩型交叉操作类似于遗传算法中的两点交叉,根据随机生成的交叉点选择对应子串,其概率分布满足指数形式,过程如下:首先随机产生一个交叉起始点,应选择变异个体$H_i(t+1)$中位于点位的分量,保证新个体$V_i(t+1)$中至少有一部分分量与父代个体的不同:然后根据概率选择位于其它各点位的分量来源,如果概率小于交叉概率CR时该点位的值从$H_i(t+1)$中的选取相应分量,否则从$X_i(t)$的中选取。
三. 代码演示
代码主要是从网上看到的,仅限参考。
//********************************************************/
// DE/rand/1/bin --差分进化算法-(基本类型)
//********************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <float.h>
/* Function definitions */
double func(double *);
int usage(char *);
/* Random number generator defined by URAND should return
double-precision floating-point values uniformly distributed
over the interval [0.0, 1.0) */
#define URAND ((double)rand()/((double)RAND_MAX + 1.0))
/* Definition for random number generator initialization */
#define INITRAND srand(time(0))
/* Usage for the program */
int usage(char *str)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-h] [-u] [-s] [-N NP (20*D)] ", str);
fprintf(stderr, "[-G Gmax (1000)]\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t[-C crossover constant, CR (0.9)]\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t[-F mutation scaling factor, F (0.9)]\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t[-o <outputfile>]\n\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\t-s does not initialize random number generator\n");
exit(-1);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
register int i, j, k, r1, r2, r3, jrand, numofFE = 0;
extern int D;
extern double Xl[], Xu[];
int NP = 20 * D, Gmax = 1000, c, index = -1, s = 1;
double **popul, **next, **ptr, *iptr, *U, CR = 0.9, F = 0.9,
min_value = DBL_MAX, totaltime = 0.0;
char *ofile = NULL;
FILE *fid;
clock_t starttime, endtime;
/* Parse command line arguments given by user */
for (i = 1; i < argc; i++)
{
if (argv[i][0] != '-')
usage(argv[0]);
c = argv[i][1];
switch (c)
{
case 'N':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
NP = atoi(argv[i]);
break;
case 'G':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
Gmax = atoi(argv[i]);
break;
case 'C':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
CR = atof(argv[i]);
break;
case 'F':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
F = atof(argv[i]);
break;
case 'o':
if (++i >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
ofile = argv[i];
break;
case 's': /* Flag for using same seeds for */
s = 0; /* different runs */
break;
case 'h':
case 'u':
default:
usage(argv[0]);
}
}
if (s) INITRAND;
/* Printing out information about optimization process for the user */
printf("Program parameters: ");
printf("NP = %d, Gmax = %d, CR = %.2f, F = %.2f\n",
NP, Gmax, CR, F);
printf("Dimension of the problem: %d\n", D);
/* Starting timer */
starttime = clock();
/* Allocating memory for current and next populations, intializing
current population with uniformly distributed random values and
calculating value for the objective function */
// NP:种群大小, Gmax:迭代次数, CR:交叉概率, F:扰动向量的缩放因子
//当前种群
popul = (double **)malloc(NP*sizeof(double *));
if (popul == NULL) perror("malloc");
//下代种群
next = (double **)malloc(NP*sizeof(double *));
if (next == NULL) perror("malloc");
//当前种群popul[NP][D+1]
for (i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
//个体维度空间分配
popul[i] = (double *)malloc((D + 1)*sizeof(double));
if (popul[i] == NULL) perror("malloc");
//初始化维度值
for (j = 0; j < D; j++)
popul[i][j] = Xl[j] + (Xu[j] - Xl[j])*URAND;
//最后的元素内存放该个体的适应度值
popul[i][D] = func(popul[i]);
numofFE++;//统计评估次数
//下一代个体空间分配
next[i] = (double *)malloc((D + 1)*sizeof(double));
if (next[i] == NULL) perror("malloc");
}
/* 为实验向量分配空间--Allocating memory for a trial vector U */
U = (double *)malloc((D + 1)*sizeof(double));
if (U == NULL) perror("malloc");
/* The main loop of the algorithm */
for (k = 0; k < Gmax; k++)
{
for (i = 0; i < NP; i++) /* Going through whole population */
{
/* Selecting random indeces r1, r2, and r3 to individuls of
the population such that i != r1 != r2 != r3 */
//1.选择三个互不相同的随机个体r1,r2,r3
do
{
r1 = (int)(NP*URAND);
} while (r1 == i);
do
{
r2 = (int)(NP*URAND);
} while (r2 == i || r2 == r1);
do
{
r3 = (int)(NP*URAND);
} while (r3 == i || r3 == r1 || r3 == r2);
jrand = (int)(D*URAND);
/* Mutation and crossover */
//2. 执行变异和交叉操作
for (j = 0; j < D; j++)
{
//执行二项式交叉
if (URAND < CR || j == jrand)
{
//试验向量部分来自变异后的向量
U[j] = popul[r3][j] + F*(popul[r1][j] - popul[r2][j]);
}
else
//试验向量部分来自个体i
U[j] = popul[i][j];
}
//3. 计算新生成向量的适应度值
U[D] = func(U);
numofFE++;
/* Comparing the trial vector 'U' and the old individual
'next[i]' and selecting better one to continue in the
next population.注意:空间的交替变换和使用 */
//贪婪策略从试验向量U和当前个体i中选择一个好的放入到下一代个体中
if (U[D] <= popul[i][D])//新向量好
{
//试验向量U牛逼, next指向当前的试验向量U,u指向next, 方法:指针交换
iptr = U;
U = next[i];
next[i] = iptr;
}
else//原始向量牛逼, next指向个体i, 方法: 直接拷贝
{
for (j = 0; j <= D; j++)
next[i][j] = popul[i][j];
}
} /* End of the going through whole population */
/* Pointers of old and new populations are swapped */
//指针交换,各指针指向的空间发生变化
ptr = popul;
popul = next;
next = ptr;
} /* End of the main loop */
/* Stopping timer */
endtime = clock();
totaltime = (double)(endtime - starttime);
/* If user has defined output file, the whole final population is
saved to the file */
if (ofile != NULL)
{
if ((fid = (FILE *)fopen(ofile, "a")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error in opening file %s\n\n", ofile);
usage(argv[0]);
}
for (i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= D; j++)
fprintf(fid, "%.15e ", popul[i][j]);
fprintf(fid, "\n");
}
fclose(fid);
}
/* Finding best individual */
for (i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
if (popul[i][D] < min_value)
{
min_value = popul[i][D];
index = i;
}
}
/* Printing out information about optimization process for the user */
printf("Execution time: %.3f s\n", totaltime / (double)CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("Number of objective function evaluations: %d\n", numofFE);
printf("Solution:\nValues of variables: ");
for (i = 0; i < D; i++)
printf("%.15f ", popul[index][i]);
printf("\nObjective function value: ");
printf("%.15f\n", popul[index][D]);
/* Freeing dynamically allocated memory */
for (i = 0; i < NP; i++)
{
free(popul[i]);
free(next[i]);
}
free(popul);
free(next);
free(U);
return(0);
}
参考:
